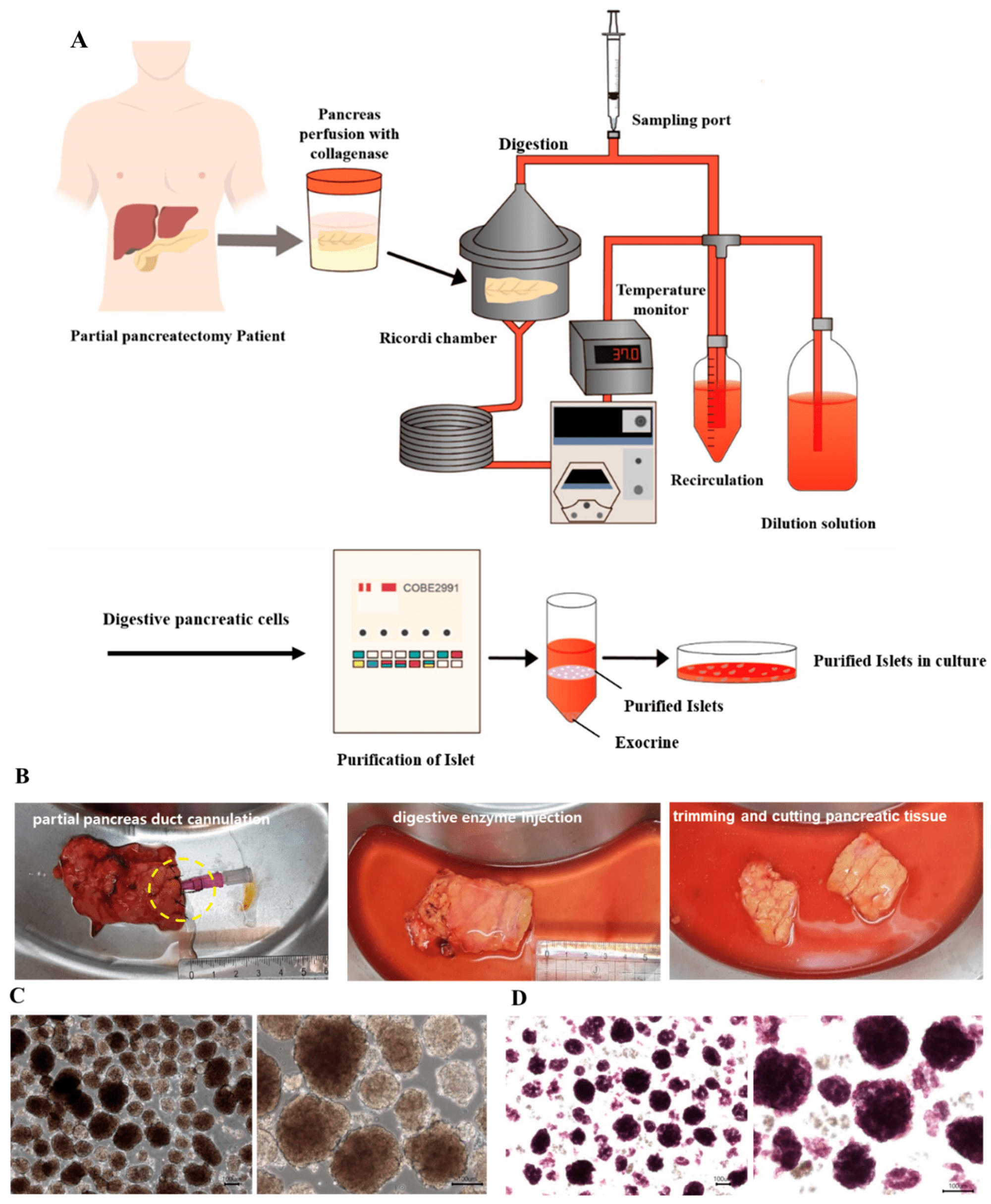
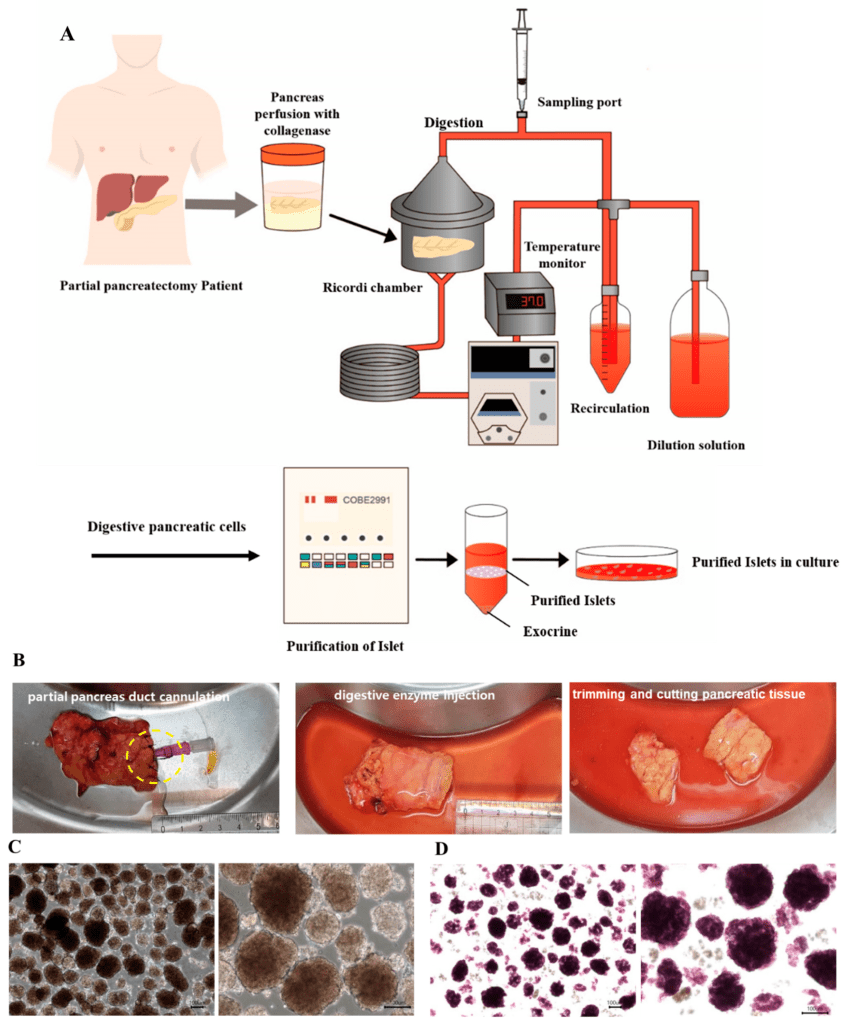
In the realm of diabetes treatment, a groundbreaking discovery has emerged, and it’s making waves in the scientific community. This revolutionary breakthrough involves the transformation of healthy human pancreas cells into laboratory-generated cells, which are then converted into a powdered form for patient injections.
This article delves into the innovative process of converting pancreatic cells into injectable powder, marking a significant diabetes treatment breakthrough.
Table of Contents
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a global health challenge that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Traditional treatment approaches, such as medication, insulin therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, have limitations in restoring normal pancreatic function. The recent discovery revolves around harnessing the potential of a healthy piece of the human pancreas to generate cells in the lab. These cells can then be transformed into an injectable powder, representing a transformative leap in diabetes research and treatment.
Transforming Pancreatic Cells into Injectable Powder
Researchers have achieved a remarkable feat by converting pancreatic cells into a powdered form. This process involves meticulous freeze-drying, resulting in a fine powder suitable for easy administration via injections. Converting the cells into an injectable powder opens up new possibilities, allowing for improved storage, convenient administration, and potentially eliminating the need for invasive procedures.
The Journey to Market Availability
The heart of this breakthrough lies in the successful conversion of pancreatic cells into a powdered form. This conversion process entails meticulous freeze-drying, resulting in a fine, easily injectable powder. This transformation brings about a host of benefits, including improved storage capabilities, convenient administration, and the potential to reduce the necessity for invasive procedures. By converting pancreatic cells into an injectable powder, scientists have paved the way for new possibilities in diabetes treatment, promising a viable alternative to traditional therapies.
The Journey to Market Availability
The critical question on everyone’s mind is when this revolutionary diabetic treatment will be available in the market. The journey from the laboratory to the market involves a series of rigorous steps. It encompasses extensive research, clinical trials, and regulatory approvals to ensure safety, efficacy, and long-term effects. While the exact timeline remains uncertain, it is imperative that these processes are diligently followed before the treatment can be widely accessible.
Benefits and Potential Applications
The transformation of pancreatic cells into injectable powder carries numerous benefits and opens doors to various potential applications in diabetes treatment. The powdered form allows for precise dosing, convenient administration, and improved patient adherence. Furthermore, it holds the promise of targeted delivery, enabling the cells to reach specific areas within the body. Additionally, the powdered cells can be stored for more extended periods and transported more efficiently, effectively addressing logistical challenges. This innovative approach may even have implications beyond diabetes treatment, potentially benefiting other medical conditions requiring cellular therapies. The versatility and convenience offered by the injectable cell powder mark a significant stride in the field of regenerative medicine.
Future Prospects and Challenges
While the conversion of pancreatic cells into injectable powder represents a remarkable breakthrough, several challenges must be overcome before market availability. Ensuring the long-term viability and functionality of the powdered cells within the body is a critical aspect that requires extensive research. Additionally, the storage, handling, and transportation of the powder necessitate careful consideration to maintain the cells’ integrity. Regulatory approval processes can also be time-consuming, involving meticulous evaluation of safety and efficacy data. The collaborative efforts of scientists, healthcare professionals, regulatory bodies, and industry stakeholders are crucial in navigating these challenges and paving the way for the eventual availability of this transformative diabetic treatment.
Conclusion
While an exact timeline for market availability cannot be definitively determined, the progress made in diabetic treatment research is promising. The transformation of pancreatic cells into injectable powder represents an innovative and patient-centric approach to diabetes management. With ongoing research, clinical trials, and regulatory processes, it is reasonable to anticipate that this groundbreaking treatment could become accessible within the next decade. As scientific advancements continue to unfold, individuals living with diabetes can hold hope for a future where their condition is managed more effectively, bringing them closer to a life of improved health and well-being. This remarkable breakthrough in diabetes treatment offers a glimmer of hope on the horizon for millions affected by this condition. For more information, so please click this link.