
In today’s digital world, cybersecurity is of utmost importance for businesses of all sizes. With the increasing reliance on technology, the volume and sophistication of cyber threats are also on the rise. In this article, we will explore why cybersecurity is important for businesses and how it can protect organizations from cyberattacks. We will discuss the various types of cybersecurity threats, the benefits of implementing cybersecurity practices, and the challenges faced in maintaining robust cybersecurity measures. For more information, so please click this link.
Table of Contents
Why is Cybersecurity Important for Business?

The importance of cybersecurity for businesses cannot be overstated. With the growing number of users, devices, and programs in modern enterprises, combined with the massive amount of data being generated, the risk of cyberattacks is higher than ever. Cybersecurity is crucial for the following reasons:
Protection against Cyberattacks and Data Breaches
Cyberattacks can have severe consequences for businesses, including financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. Implementing cybersecurity measures helps protect organizations from these attacks and minimizes the risk of data breaches.
Safeguarding Data and Networks
Data is a valuable asset for businesses, and protecting it from unauthorized access is paramount. Cybersecurity ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, safeguarding it from theft, alteration, or destruction. It also protects networks from unauthorized access, preventing potential breaches.
Prevention of Unauthorized User Access
Unauthorized access to systems and networks can lead to data breaches and other security incidents. Cybersecurity measures, such as strong authentication protocols and access controls, help prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to sensitive information or critical systems.
Improved Recovery Time after a Breach
In the event of a cybersecurity incident, having robust cybersecurity measures in place can help organizations recover more quickly. A well-prepared incident response plan, regular backups, and effective recovery strategies can minimize the impact of a breach and reduce downtime.
Protection for End Users and Endpoint Devices
Endpoint devices, such as computers, laptops, and mobile devices, are often targeted by cybercriminals. Implementing endpoint security measures, such as antivirus software and encryption, protects end users from malware and other threats.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries are subject to regulations that require organizations to implement specific cybersecurity measures. Compliance with these regulations ensures that businesses meet legal requirements and mitigate the risk of penalties or legal consequences.
Business Continuity
Maintaining cybersecurity measures is essential for business continuity. Cyberattacks can disrupt operations, causing downtime and financial losses. By protecting systems and data, businesses can ensure the continuity of their operations and minimize the impact of potential disruptions.
Improved Reputation and Trust
A strong cybersecurity posture enhances a company’s reputation and builds trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders. Demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity shows that an organization takes the protection of sensitive information seriously, which can lead to increased customer loyalty and business opportunities.
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
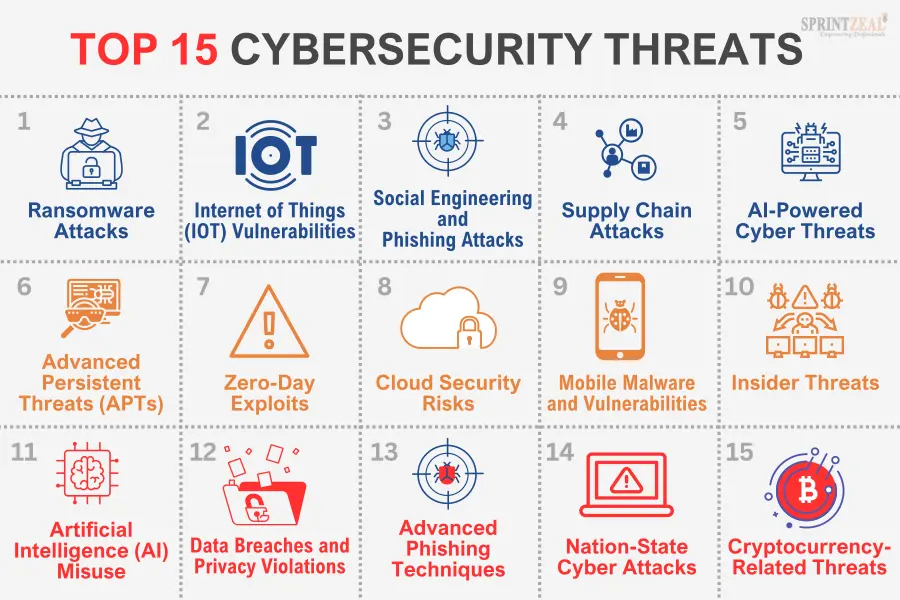
Cybersecurity threats come in various forms, each with its own characteristics and potential impact. Understanding these threats is crucial for organizations to develop effective cybersecurity strategies. Some common types of cybersecurity threats include:
Malware
Malware is malicious software designed to harm computer systems or steal sensitive data. It includes viruses, worms, trojans, and spyware. Cybercriminals use malware to gain unauthorized access, disrupt operations, or steal valuable information.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data and demands a ransom for its release. It can cause significant financial and operational damage, as organizations may be forced to pay the ransom or face the loss of critical data.
Phishing
Phishing is a social engineering attack where cybercriminals trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details. They often impersonate reputable organizations or individuals through fraudulent emails or websites.
Insider Threats
Insider threats are security breaches caused by individuals within an organization who misuse their authorized access. These threats can be intentional or accidental and may result in data breaches or other security incidents.
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks involve overwhelming a target system with a flood of traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users. These attacks disrupt services and can cause significant financial losses.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are prolonged and targeted attacks where cybercriminals infiltrate a network and remain undetected for extended periods. Their goal is to steal sensitive data or wreak havoc within the targeted organization.
Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology to manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. Common social engineering techniques include phishing, pretexting, and baiting.
These are just a few examples of the many cybersecurity threats organizations face. It is essential to stay updated on the latest threats and vulnerabilities to develop effective defenses.
Benefits of Cybersecurity
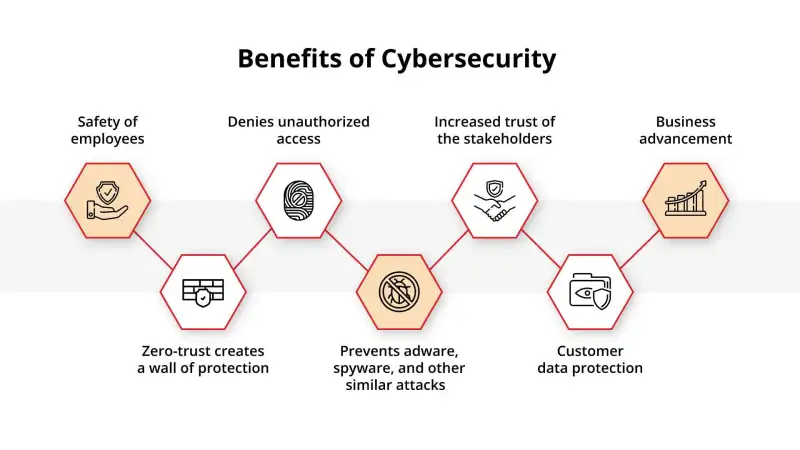
Implementing and maintaining strong cybersecurity practices offer several benefits for organizations. Some key benefits include:
Protection against Cyberattacks and Data Breaches
Cybersecurity measures help safeguard organizations against cyberattacks and minimize the risk of data breaches. By implementing robust security controls, organizations can detect and mitigate threats effectively.
Safeguarding Data and Networks
Cybersecurity ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and protects networks from unauthorized access. This helps prevent unauthorized modifications, theft, or destruction of sensitive information.
Prevention of Financial Losses
Cyberattacks can result in significant financial losses for organizations. By investing in cybersecurity, businesses can minimize the financial impact of security incidents, such as data breaches or ransomware attacks.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with cybersecurity regulations is essential for organizations operating in regulated industries. By implementing cybersecurity measures, businesses can meet legal requirements and avoid penalties or legal consequences.
Enhanced Business Reputation and Trust
A strong cybersecurity posture enhances an organization’s reputation and builds trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders. Demonstrating a commitment to protecting sensitive information can lead to increased customer loyalty and business opportunities.
Business Continuity
By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, organizations can ensure the continuity of their operations. Effective incident response plans and recovery strategies help minimize downtime and mitigate the impact of cyber incidents.
Protection for End Users and Endpoint Devices
Endpoint security measures protect end users and their devices from malware and other threats. This helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information and ensures the security of personal and business data.
Increased Employee Productivity
A secure IT environment provides employees with the confidence to perform their duties without the fear of cyber threats. This allows them to focus on their work and be more productive, contributing to the overall success of the organization.
Competitive Advantage
Investing in cybersecurity can provide a competitive advantage. Organizations with strong security measures may be more attractive to customers and partners who value the protection of their data and information.
Challenges in Maintaining Cybersecurity
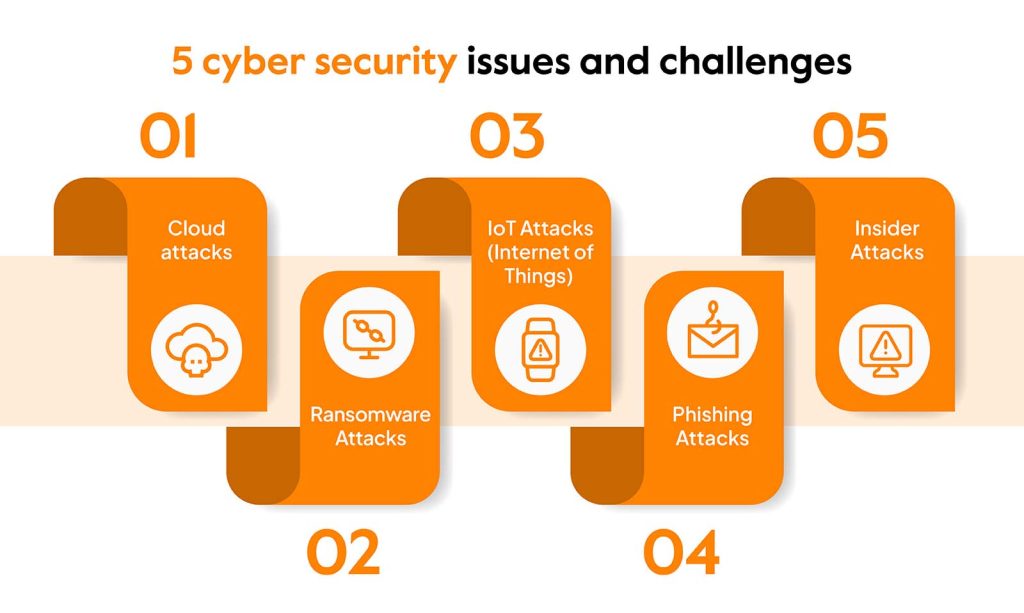
Maintaining robust cybersecurity measures is a constant challenge for organizations. Some of the key challenges include:
Evolving Threat Landscape
Cyber threats are continuously evolving, and new attack techniques emerge regularly. Keeping up with these threats and updating security measures to address them is a constant challenge for organizations.
Data Deluge
The increasing volume of data collected and stored by organizations poses a challenge for cybersecurity. Protecting sensitive information from cybercriminals who seek to steal or misuse it requires robust security measures and effective data management practices.
Cybersecurity Awareness Training
Employees play a crucial role in maintaining cybersecurity. However, human error is a significant contributing factor to security incidents. Providing cybersecurity awareness training to employees is essential to educate them about potential risks and teach them how to prevent security breaches.
Workforce Shortage and Skills Gap
The demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals exceeds the available talent pool. Organizations struggle to find qualified individuals to fill cybersecurity roles, leading to a workforce shortage. Bridging the skills gap and attracting top talent is a challenge for many organizations.
Supply Chain and Third-Party Risks
Businesses often rely on third-party vendors and suppliers, increasing the risk of cybersecurity incidents. Organizations must assess and manage the cybersecurity posture of their partners to ensure the security of their data and systems.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity. Organizations must stay updated on the latest threats, invest in training and development programs, and collaborate with industry partners to enhance cybersecurity measures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cybersecurity is vital for businesses to protect their systems, data, and operations from cyber threats. By implementing strong cybersecurity practices, organizations can safeguard their assets, maintain customer trust, and mitigate the financial and reputational risks associated with cyberattacks. However, maintaining robust cybersecurity measures is an ongoing challenge in the face of evolving threats, the growing volume of data, and the shortage of skilled professionals. Organizations must remain vigilant, adapt to new security risks, and invest in comprehensive cybersecurity strategies to stay ahead of cybercriminals. For more information, so please click this link and this link also.
