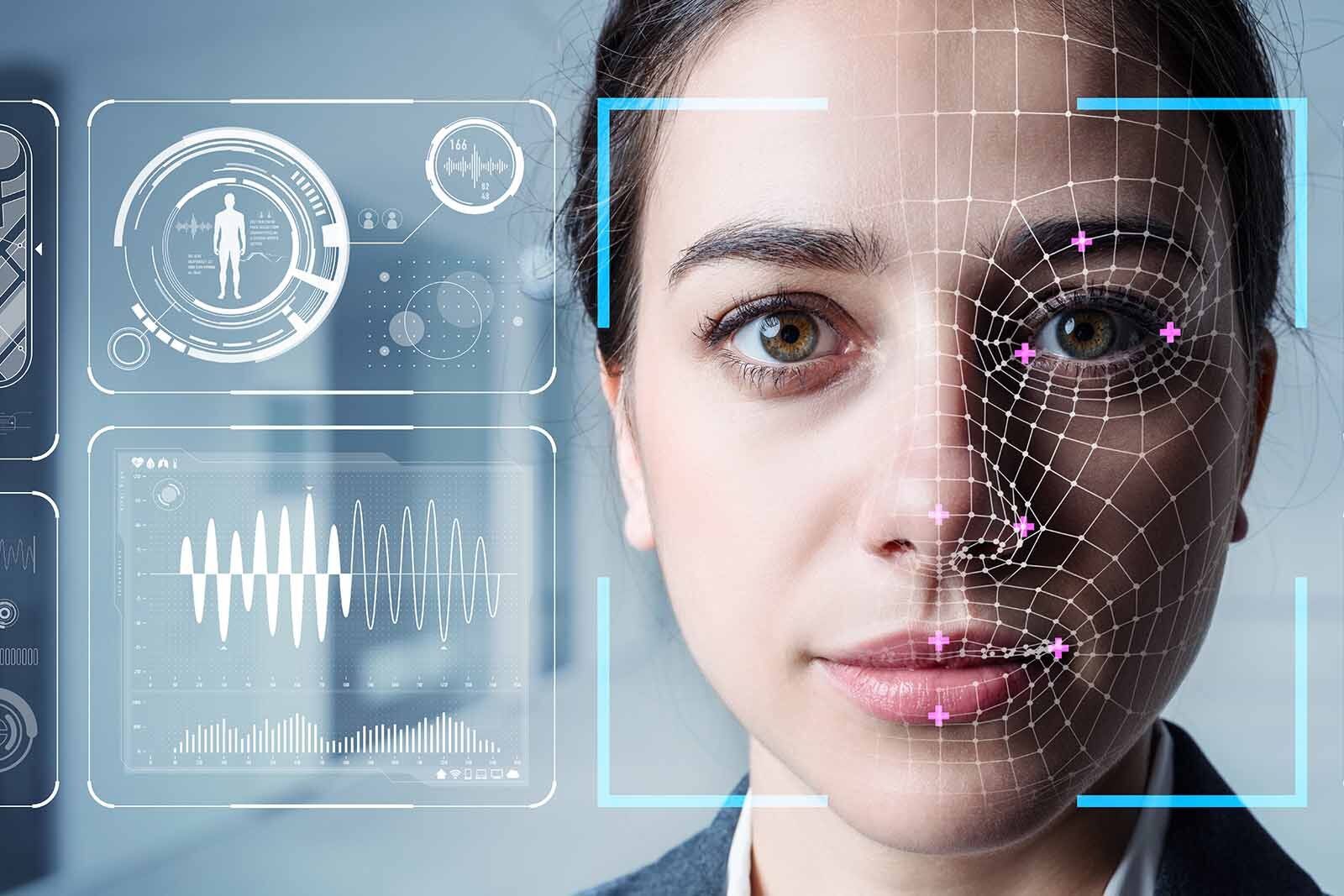
You may think that biometrics in technology is the ultimate solution for your security and privacy. After all, biometrics uses your unique physical and behavioral characteristics to identify and authenticate you, such as your fingerprints, face, voice, or iris. No one can steal or fake your biometrics, right?

Wrong!
In this article, we will reveal some shocking secrets about biometrics in technology that will make you rethink your trust in this technology. You will discover how biometrics can be hacked, spoofed, stolen, or abused by hackers, criminals, governments, and corporations. You will also learn how biometrics can violate your privacy, expose your personal information, and even endanger your life.
Table of Contents
How Biometrics Can Be Hacked
Biometrics in technology may seem secure and reliable, but they are not immune to hacking. Hackers can use various methods to bypass, compromise, or manipulate biometric systems, such as:

- Spoofing: This is the act of creating fake biometric samples or artifacts to fool biometric scanners. For example, hackers can use photos, videos, masks, prosthetics, or 3D-printed models of your face to trick facial recognition systems. They can also use fake fingerprints, finger molds, or gummy bears to fool fingerprint scanners.
- Replay attacks: This is the act of capturing and replaying biometric data to biometric systems. For example, hackers can use malware, phishing, or social engineering to obtain your biometric data from your devices or online accounts, and then use them to access your accounts or services.
- Database breaches: This is the act of stealing or leaking biometric data from databases or servers. For example, hackers can exploit vulnerabilities, use ransomware, or launch cyberattacks to access biometric databases that store millions of biometric records of users. They can then use or sell these data for malicious purposes.
- Template attacks: This is the act of modifying or tampering with biometric templates or algorithms. For example, hackers can use reverse engineering, machine learning, or artificial intelligence to alter or corrupt biometric templates or algorithms, and then use them to generate fake or altered biometric data.
How Biometrics Can Violate Your Privacy
Biometrics in technology may seem convenient and user-friendly, but they can also pose serious threats to your privacy. Biometrics can reveal sensitive and personal information about you, such as:

- Your identity: Biometrics can be used to identify you and link you to your online and offline activities, such as your browsing history, social media posts, purchases, locations, contacts, and preferences. This can create a detailed profile of you that can be used for targeted advertising, surveillance, or discrimination.
- Your health: Biometrics can be used to detect and diagnose your health conditions, such as your heart rate, blood pressure, stress level, mood, or diseases. This can expose your medical history, genetic traits, or mental state that can be used for insurance, employment, or social stigma.
- Your emotions: Biometrics can be used to measure and analyze your emotions, such as your happiness, sadness, anger, or fear. This can reveal your psychological state, personality, or behavior that can be used for manipulation, persuasion, or coercion.
How Biometrics Can Endanger Your Life
Biometrics in technology may seem harmless and benign, but they can also put your life at risk. Biometrics can be used to harm or kill you, such as:

- Biometric weapons: These are weapons that use biometrics to target or activate. For example, biometric guns can use fingerprints or facial recognition to unlock or fire, biometric bombs can use voice or iris recognition to detonate, or biometric drones can use biometric data to track or attack.
- Biometric ransom: This is the act of holding your biometrics hostage or demanding a ransom for them. For example, hackers can use biometric malware or devices to lock or encrypt your biometric data, and then ask for money or other favors to unlock or decrypt them.
- Biometric mutilation: This is the act of injuring or removing your biometric features or organs. For example, criminals can use violence or torture to cut off your fingers, pluck out your eyes, or rip off your face to access your biometric devices or accounts.
How to Protect Yourself from Biometrics
Biometrics in technology is not as secure and private as you may think. Biometrics can be hacked, spoofed, stolen, or abused by various actors and methods. Biometrics can also violate your privacy, expose your personal information, and even endanger your life.
So, what can you do to protect yourself from biometrics?
Here are some tips and best practices to follow:

- Use biometrics with caution: Biometrics can be useful and convenient, but they can also be risky and intrusive. Use biometrics only when necessary, and only with trusted and reputable biometric systems and providers. Avoid using biometrics for sensitive or critical applications, such as banking, voting, or health care.
- Use biometrics with other factors: Biometrics can be compromised or spoofed, so they should not be used alone. Use biometrics with other factors of authentication, such as passwords, PINs, or tokens. This can provide an extra layer of security and prevent unauthorized access to your biometric devices or accounts.
- Use biometrics with consent: Biometrics can reveal personal and private information about you, so they should not be used without your consent. Use biometrics only with your permission, and only with clear and transparent policies and terms. Avoid using biometrics with unknown or suspicious biometric systems or providers, or with hidden or unclear biometric purposes or consequences.
- Use biometrics with protection: Biometrics can be stolen or leaked, so they should be protected. Use biometrics with encryption, anonymization, or deletion. This can prevent your biometric data from being accessed, copied, or misused by hackers, criminals, governments, or corporations.
Conclusion
Biometrics in technology is not as unbelievable as you may think. Biometrics can unveil jaw-dropping secrets about your security and privacy that will make you rethink your trust in this technology. Biometrics can be hacked, spoofed, stolen, or abused by various actors and methods. Biometrics can also violate your privacy, expose your personal information, and even endanger your life. For more information, so please visit this link, hacking-the-future-with-cybersecurity.
Therefore, you should be aware and careful of the risks and challenges of biometrics in technology, and take the necessary steps and measures to protect yourself from biometrics.
1: What is Biometrics? How is it used in security? – Kaspersky
2: How to fool facial recognition systems – BBC Future
3: How to hack a fingerprint sensor – Naked Security
4: Replay Attacks: How to Prevent Them – Auth
How It Happens and How to Prevent It – Keeper Security : Template Attacks on Biometric Systems – SpringerLink : Biometrics and Privacy – Privacy International : Biometrics and Health Data – Biometric Update : Biometrics and Emotions – Biometric Technology Today : Biometric Weapons – The Atlantic : Biometric Ransomware – Security Boulevard : Biometric Mutilation – The Guardian
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
1. Is biometrics in technology really as secure as it seems?
Biometrics in technology may offer convenience and security, but they’re not infallible. Despite using unique physical and behavioral traits for identification, biometric systems can be hacked, spoofed, or compromised.
2. How can biometrics be hacked?
Hackers can employ various methods to bypass or manipulate biometric systems, including spoofing, replay attacks, database breaches, and template attacks. These techniques can allow unauthorized access to biometric-protected devices or services.
3. What are the privacy concerns associated with biometrics?
Biometric data can reveal sensitive personal information, such as identity, health status, and emotional state. This information can be exploited for targeted advertising, surveillance, or discrimination, raising significant privacy concerns.
4. Can biometrics pose physical risks to individuals?
Yes, biometric technology presents potential physical risks. Biometric weapons, biometric ransom, and biometric mutilation are examples of how biometric data can be used to harm or endanger individuals.
5. How can individuals protect themselves from biometric vulnerabilities?
To mitigate risks associated with biometrics, individuals should use biometric systems cautiously, employ additional authentication factors, give consent for biometric usage, and ensure their biometric data is protected with encryption and other security measures.

